X-ray Telescopes
by eschellhase
Light comes at many different wavelengths and energies. The light we see represents light with wavelength from about 400 to 700 nanometers. Infrared light and radiowaves have longer wavelengths (and thus carry less energy) than visible light, while UV rays and x-rays and gamma rays have shorter wavelengths (and carry higher energy). Even though we can only see the visible spectrum, we can build instruments that detect the other sorts of light. Radios pick up radio waves and x-ray imaging at the doctor’s office detects where x-ray light has been allowed to pass through the body.
In astronomy looking at the different wavelengths of light can tell us more about the Universe. For this reasons different sorts of telescopes have been designed. Visible light telescopes are considered normal telescopes, but there are also radiowave telescopes, infrared telescopes, ultraviolet telescopes, x-ray telescopes, and gamma ray telescopes. To observe the different lights the telescopes have to be built in a certain way and sometimes put in a certain location. Since gamma rays, x rays, and infrared light do not penetrate our atmosphere to the surface, telescopes observing these types of light must be launched into high in the sky or into outerspace.
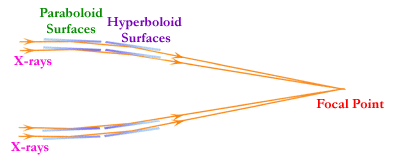
X-ray light is hard to catch. Normal mirrors do not reflect x-ray light, rather the high-energy light simply penetrates the mirror. However, if the mirror is placed at an angle to the light the light will reflect. Many people compare this to shooting a bullet. If you shoot a bullet directly at a metal sheet, the bullet is just going to dent the sheet. But if you just let the bullet graze the sheet, the bullet will reflect off the sheet. So called grazing incidence mirrors focus the x-ray light so that an image can be constructed. This is part of what makes x-ray telescopes different from other telescopes. Many telescopes varying in mission and construction have been sent into space built on this concept.
XRTs (x-ray telescopes) have allowed us to observe phenomena we otherwise would not have known about or understood as well. The first x-ray telescopes were used to observe the sun. We have also been able to observe the heat distribution between galaxies, detect neutron stars and black holes, and examine supernova remnant expansion.

Wow, I didn’t think that X-rays would penetrate a mirror! Out of curiosity, are the mirrors made out of a different reflective substance than mirrors that reflect visible light?
X-ray telescope mirrors are often made out of gold or iridium, but they can also be made out of metal foil and ceramics. Basically you want a dense material. The angle you put the mirrors at depends on what they are made out of. I think visible mirrors are normally silver coated or aluminized. But I don’t think the two types of mirrors for telescopes necessarily have to be made of separate materials. See X-ray Optics for more detailed info.